CyberYard CTF – Muzan
Do you think you’ve chased me down?
Muzan Reverse (Windows x64) Write-up
Category: Reverse
Prompt:Do you think you’ve chased me down?
Artifact: ⬇️ Muzan.zip - (PE, x64)
Flag format:FlagY{...}
intro
The binary reads a 40-byte flag, splits it into 10 big-endian DWORDs, derives two per-run masks, rebuilds five 64-bit values from your input, and compares them to five hardcoded QWORDs.
By using the known prefix FlagY{ and brute-forcing two bytes after {, we recover the masks and reconstruct the full flag:
1
FlagY{ab8624a5fa40359d8fb595baf3af88334}
Challenge Description
You’re given a Windows x64 executable that prints:
1
Enter The Flag:
If you’re wrong, it prints:
1
Wrong Flag :(
On success:
1
Correct Flag :)
Initial Recon
Strings:
Enter The Flag:Wrong Flag :(Correct Flag :)
Control flow:
mainis a tailcall intofun_140009000, where all the logic lives.
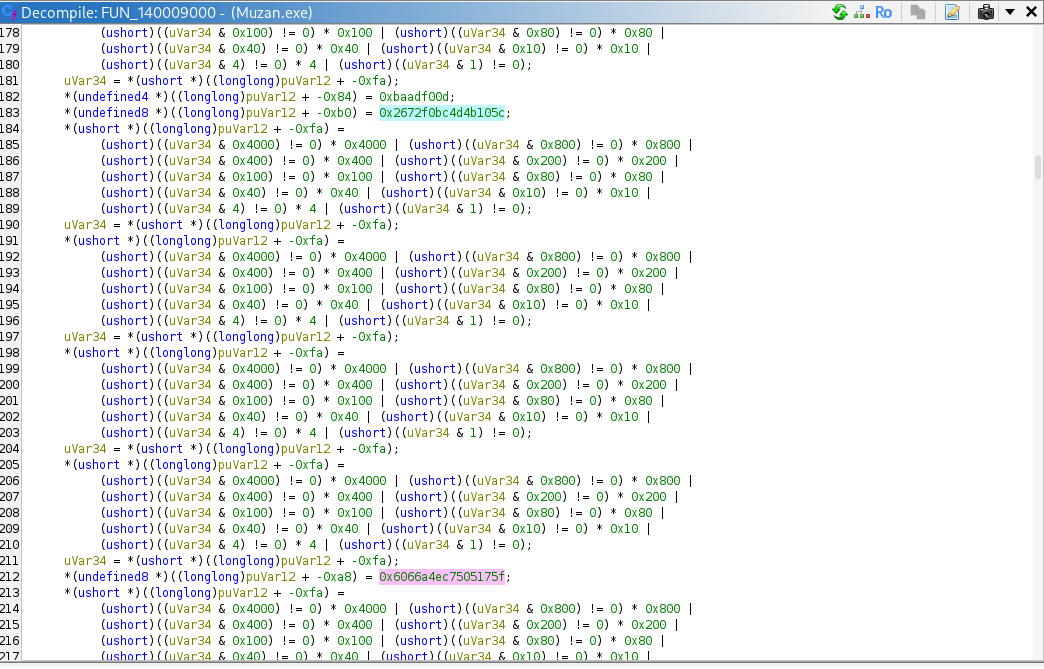
Hardcoded targets (QWORDs):
1
2
3
4
5
0x2672F0BC4D4B105C
0x6066A4EC7505175F
0x3431FBEA2D544958
0x3931AFBF7651170D
0x6B30FCFC27034543
24-byte blob copied with memcpy:
1
2
CE FA ED FE BE BA FE CA BE BA AD DE
5E EA 15 0D ED A5 CE DE 1D AC AD BA
This blob and a rand() seed help derive round state, but the final verification reduces to simple XOR relations with two constants reused across pairs.
What the Program Actually Does (Simplified)
- Reads exactly 40 ASCII bytes (no spaces).
Splits them into 10 big-endian 32-bit words:
1
D0_0, D1_0, D0_1, D1_1, …, D0_4, D1_4
Derives two 32-bit masks (per execution, but constant across all pairs):
1
K_lo, K_up
For each pair
i = 0..4, forms a 64-bit value:1 2 3
L[i] = D1_i ^ K_lo # lower 32 bits U[i] = D0_i ^ D1_i ^ K_up # upper 32 bits Q'[i] = (U[i] << 32) | L[i]
- Compares
Q'[i]against the hardcoded QWORD #i. Any mismatch →Wrong Flag :(. All match →Correct Flag :).
Key point: It’s linear XOR per pair, with two unknowns (K_lo, K_up) that are the same for all five pairs.
plan of exploit
- We know the format:
FlagY{...}and it closes with}. - That fixes the first 4 bytes D0_0 = “Flag”.
- The next 4 bytes D1_0 = “Y{“ + ?? + ?? (two unknown bytes).
From the first target
Q[0] = (U0 << 32) | L0:1 2
K_lo = L0 ⊕ D1_0 K_up = U0 ⊕ D0_0 ⊕ D1_0
- Brute-force the two unknown bytes (65,536 candidates), compute
K_lo/K_up, rebuild all pairs, and accept the result that:- starts with
FlagY{, ends with}, - and the payload inside braces is hex (natural for this chall).
- starts with
This yields a unique clean ASCII flag.
Solver
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Q=[0x2672F0BC4D4B105C,0x6066A4EC7505175F,0x3431FBEA2D544958,0x3931AFBF7651170D,0x6B30FCFC27034543]
U=[q>>32 for q in Q]; L=[q&0xffffffff for q in Q]
D0_0=int.from_bytes(b"Flag","big")
hexs=set("0123456789abcdef")
for a in range(256):
for b in range(256):
D1_0=int.from_bytes(b"Y{"+bytes([a,b]),"big")
K_lo=L[0]^D1_0; K_up=U[0]^D0_0^D1_0
out=bytearray()
for i in range(5):
D1=L[i]^K_lo; D0=U[i]^D1^K_up
out+=D0.to_bytes(4,"big")+D1.to_bytes(4,"big")
try: s=out.decode("ascii")
except: continue
if s.startswith("FlagY{") and s.endswith("}") and all(c in hexs for c in s[7:-1]):
print(s); raise SystemExit
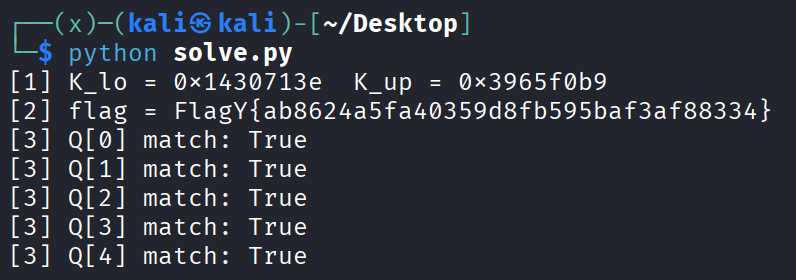
Output:
1
FlagY{ab8624a5fa40359d8fb595baf3af88334}